Warning: Trying to access array offset on value of type bool in /var/www/foxof.com/wp-content/plugins/all-in-one-schemaorg-rich-snippets/functions.php on line 982
Warning: Trying to access array offset on value of type bool in /var/www/foxof.com/wp-content/plugins/all-in-one-schemaorg-rich-snippets/functions.php on line 982
Warning: Trying to access array offset on value of type bool in /var/www/foxof.com/wp-content/plugins/all-in-one-schemaorg-rich-snippets/functions.php on line 982
Warning: Trying to access array offset on value of type bool in /var/www/foxof.com/wp-content/plugins/all-in-one-schemaorg-rich-snippets/functions.php on line 984
Warning: Trying to access array offset on value of type bool in /var/www/foxof.com/wp-content/plugins/all-in-one-schemaorg-rich-snippets/functions.php on line 984
Warning: Trying to access array offset on value of type bool in /var/www/foxof.com/wp-content/plugins/all-in-one-schemaorg-rich-snippets/functions.php on line 984
Home / Heating / Infrared Heating / Focus on far infrared heater or FIR (español – français)
Heating principle of a far infrared radiant emitter
Share this page
Why do we talk about “far” radiation FIR?

The infrared radiation of the sun is the “part” of the light which heats the earth (not to be confused with the UV). This radiation is invisible to humans. For all that, when our body receives its radiation, we feel a sensation of heat (and often of well-being).
We can draw 3 teachings out of that: the heat is thus transmitted “without contact”, indoor as outdoor, even if the surrounding air is cold (for exemple winter skiing). There is no need to heat the ambient air to feel the heat. The heat is felt by the human body when the radiation hits the skin.
Indeed, for a given wavelength (and depending on the efficiency of the heater), the “range” of the radiation will be more or less significant (or long). It is for this reason that we distinguish between the far infrared (or long) and other types of infrared, whose applications are different.
The heaters called “far infrared” are heat emitters reproducing the radiation of the sun in a very specific wavelength, adapted exclusively for domestic indoor heating.

PS: the best far infrared heaters have a range between 4 and 5 meters around the heater (in all directions), whereas those emitting little infrared are limited to 50 cm (e.g. low-end radiants). It is then possible with this technology, and a proper positioning of the heater, to reach all the room zones to be heated.
Summary table of infrared applications based on the wavelength
3 different types of infrared for a multitude of applications
| 1) NIR = Near Infrared Radiation or Rays |
750 nm–1400 nm. Telecommunication. Night vision. Spectroscopy. Motion detectors, etc. |
| 2) MID = Mid Wavelength Infrared |
between 1400 nm–3000 nm. Telecommunication. Thermal imagery. Military applications (ballistic guide). Heating for workshops or warehouses. Industry (drying, molding, welding, cutting). |
| 3) FIR = Far Infrared Radiation or Rays classified in the IR-C category |
IR-C from 3000 nm (3 µm) to 1 mm. Medical applications, sauna, some heaters for warehouses or workshops, etc. =>> FIR = Far Infrared from 15 µm to 1 mm => Medical applications and Indoor Heating. |
Source: classification of the International Commission on Illumination (CIE)
Infrared wavelength range is from 700 nm to 1 mm.
Why should we use Far Infrared in domestic heating applications?
The IR-C, due to their qualities, do not penetrate deep into human skin (only a few millimeters). However, due to the heat absorption coefficients of the materials (absorption range between 2 and 20 µm), the far infrared is particularly well suited for the heating of buildings.
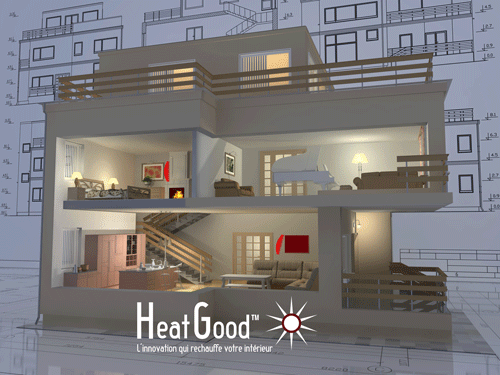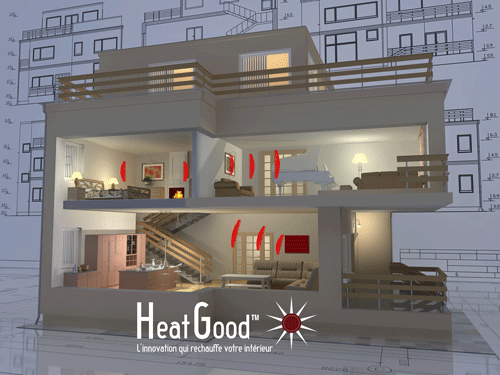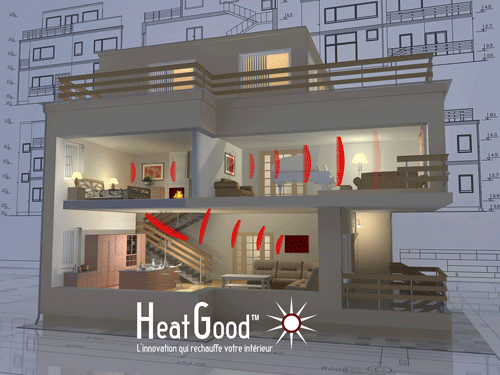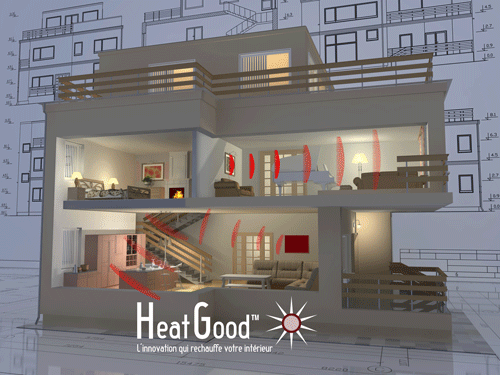
Illustration of the FIR Far Infrared Radiation for domestic heating / source: heatgood.com
Popular articles about Heating by Far Infrared Heaters
To know more: Article How to increase the perceived temperature in a heated room without increasing the bill?
See the testimony of domain experts: Conventional wisdom concerning the infrared heaters
FOX38







