Home / Heating / Infrared Heating / Radiant temperature measurement (español – français)
How to evaluate or measure the radiant or apparent temperature?
Share this page
Impacts of heat transfer by radiation within the framework of the heating
The greater the difference between the temperature of our body and the surrounding temperature is, the more the heat flow (amount of heat coming out from our body toward the environment) increases. This is why, even in a room heated to 22°C, if you put yourself in front of a cold wall (stone wall, simple glazing façade, etc.) you can feel an intense cold and a situation of discomfort.
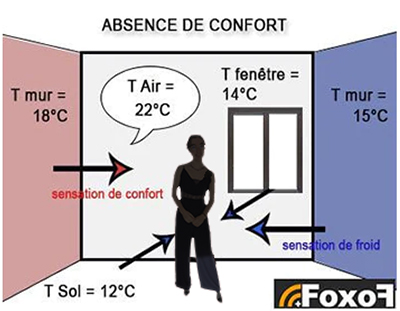
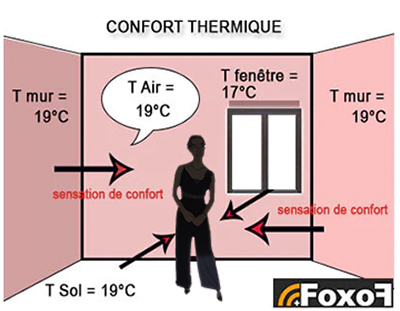
Also to achieve the thermal comfort in the buildings (according to the standard ISO 7730:2005 Ergonomics of the thermal environment), we must fight against the radiation asymmetry of different walls (glazings, walls, ceiling, floor). This should not be greater than 10°C between the coldest and the warmest wall. However the discomfort can be felt even when there is 7-8°C of difference.
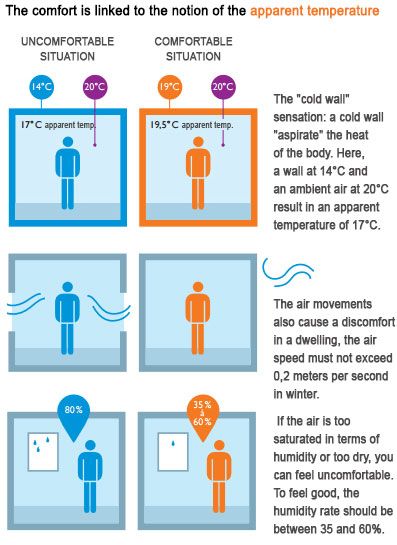
Apparent temperature explanation according to french organisation ADEME
Heating by infrared radiation
In contrast to the heating by convection which heats the air, the heating by radiation heats the masses (wall, floor, ceiling, objects) and allows the structure of the building to accumulate the energy and then to release it at low temperature. The wall temperature is raised, which is a critical component in achieving the thermal comfort.

Radiation effectiveness measurement
The heating by radiation brings many advantages. But you still need to choose a heating whose radiation rate is grater than 50%. Below this figure, the radiation is limited to a range too short to be able to reach all the areas of the room. The terminology of radiation should not even be allowed for that kind of heating.

The second key point is the optimal positioning of the heater so that its radiation can reach the opposite walls, the floor, the ceiling, and thus to limit the influence of cold walls. In a dwelling, you should prefer a radiant heating by far infrared – of quality – specifically designed to generate infrared radiation with a range of up to 4-5 meters.
How do we calculate the apparent temperature perceived by humans?
Empirically, inside of a room, the apparent temperature perceived by a human body (or resultant temperature) is the average between the air temperature and the average wall temperature of the room (average radiant temperature). For example: Temperature of all walls (wall, floor, ceiling) = average T of all walls = 17°C and Temperature of air Tair = 22°C. The apparent temperature in the middle of the room will be 19.5°C ((17°C+22°C)/2).
When talking about heating of industrial and commercial premises there are metrology devices whose objective is the measurement of radiating component according to the positions of the heat emitter in the premise. This equipment allows to detect and eliminate cold spots, so to improve the comfort and the consumption, especially in large premises.


The measurement is based on the technology of the black bulb sensors (black bulb spherical sensors (standard ISO7726)). The room radiation temperature sensor determines the proportion of the radiation that has a real effect or an effective radiant heat on the measurement location. We also refer to the globe-thermometer probe when measuring radiant heat. This type of probe is particularly used in the heating and the climatic engineering for the temperature measurement of large rooms (industrial hall, commercial hall, logistic warehouses, etc.).
Combined with the regulation system of radiant heat emitters, these probes affect the comfort improvement and the optimisation of consumption.
Execution :
The series of measurement is carried out 30 minutes after the stabilisation of the probe.
The measured value is Tg = measured temperature of the black globe. This value is used to calculate the average temperature of the radiation Tr.
Complementary use:
This equipment is used within the framework of professional thermal risks measurement of staff at work according to the standard NF EN 27243. The WBGT sensors (Wet-Bulb Globe Temperature or black wet-bulb sensor) realise an estimation of the thermal stress by assessing the average effect of heat on a man for a representative period of its activity. The equipment determines wether the subject is able to work in a given environment over a period of 8 hours. Inside of buildings without solar gain WBGT = 0,7 T humid + 0,3 Tg black globe temperature.
REGELTECHNIK

A German company (Nuremberg) which markets metrology elements (modbus, room temperature sensors, humidity sensors, light sensors, pressure sensors, regulators, etc.).
Room radiation temperature sensor, Model THERMASGARD RSTF
THERMASGARD hall effect resistance thermometer of RSTF type with a passive output. Specifically designed to measure the temperature in large rooms and industrial halls, it determines the proportion of the radiation that has a real effect or an effective radiant heat on the measurement location.

black bulb sensors
TITEC GMBH

German manufacturer of metrology elements (modbus, room temperature sensors, humidity sensors, light sensors, movement sensors, pressure sensors, regulators, etc.).
Room radiant temperature resulting probe, Black Bulb model
Suspended sensor particularly suitable for high ceilings of large rooms and industrial halls. To be connected to a control and recording unit.

FOX1


